
UPDATE TO .NET FRAMEWORK 4.7.2
13 September 2019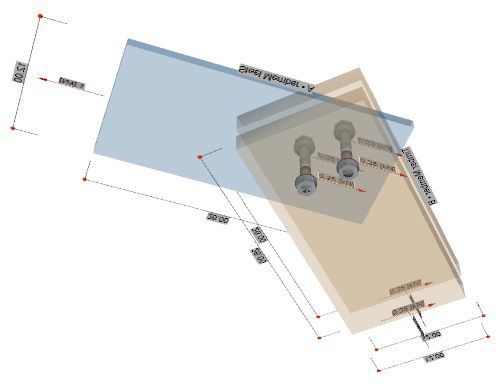
Design considerations for laterally loaded connections in APF WoodJoint
23 November 2020THE EUROCODES, european standards for structural design

Purpose of eurocodes
In 1975, the Commission of the European Community decided on an action programme in the field of construction with the objective to eliminate technical obstacles to trade and the harmonisation of technical specifications within the member states.
For fifteen years the Commission conducted the development of the Eurocodes programme, which led to the first generation of European codes in the 1990s.
The Commission decided then to transfer the preparation and the publication of the Eurocodes to the European Committee for Standardization (CEN), in order to provide them with a future status of European Standard (EN).
The Eurocodes
The eurocodes are the ten European standards (EN harmonised technical rules) specifying how structural design should be conducted within the European Union (EU). Ten eurocodes have been developed and published, each having a number of parts:
- EN 1990 Eurocode: Basis of Structural Design (establishes principles and requirements for the safety, serviceability and durability of structures, describes the basis for their design and verification and gives guidelines for related aspects of structural reliability.)
- EN 1991 Eurocode 1: Actions on structures (densities and environmental actions on structures)
- EN 1992 Eurocode 2: Design of concrete structures (specifies technical rules for the design of concrete, reinforced concrete and prestressed concrete)
- EN 1993 Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures
- EN 1994 Eurocode 4: Design of composite steel and concrete structures
- EN 1995 Eurocode 5: Design of timber structures
- EN 1996 Eurocode 6: Design of masonry structures (mortar units)
- EN 1997 Eurocode 7: Geotechnical design (engineering behaviour of earth materials)
- EN 1998 Eurocode 8: Design of structures for earthquake resistance (seismic action and rules for building)
- EN 1999 Eurocode 9: Design of aluminium structures
The national standard bodies are responsible for implementing and issuing a National Annex to the Eurocodes which will need referencing for a particular country.
What do we use Eurocodes for?
The purpose of the eurocodes is to provide:
- a means to prove compliance with the requirements for mechanical strength and stability and safety in case of fire
- a basis for construction and engineering contract specifications
- a framework for creating harmonized* technical specifications for building products (EN and ETA)
*A public standards organization whose mission is to foster the economy of the European Union by maintaining and developing coherent sets of standards and specifications.
The purpose of the Eurocodes is to identify common regulations for the following fields:
- design of common structures
- design of complex structures
- designing of traditional or innovative structures
National Annex
The National Annex (NA) is an essential document containing the entire the text of the Eurocode as published by the CEN. It specifies the parameters of civil engineering structures for each nation, such as
- the individual nation’s factors (geography, climate,…)
- application of informative annex
- procedure to adopt in the cases described by the Eurocode
- reference to complementary information that helps reinforce Eurocode status
- specific national values that are otherwise outlined in the Eurocode
- specific national values for which the Eurocode offers alternatives
Applying Eurocodes
Although the NA may specify the value of partial factors to be applied to actions and resistances, in many cases it simply accepts the value recommended in the Eurocode text. In Italy, Eurocodes are enforced as of ministerial decree of 31 July 2012. The guidance given in a National Annex applies to structures that are to be constructed within that country. National Annexes are likely to differ between countries within Europe. The National Annexes for the country where the structure is to be constructed should always be consulted in the design of a structure, such as NTC 2008/2018 for Italy.
APF Nexus is concerned with the following extract of the Eurocodes.
Eurocode – General criteria for structural design
- UNI EN 1990:2006
Eurocode 1 – Actions on structures
- UNI EN 1991-1-1:2004 Part 1-1:
- General actions – Densities, self weight, imposed loads for buildings
- UNI EN 1991-1-2:2004 Part 1-2:
- General actions – Actions on structures exposed to fire
- UNI EN 1991-1-3:2004 Part 1-3:
- General actions – Snow loads
- UNI EN 1991-1-4:2005 Part 1-4:
- General actions – Wind actions
- UNI EN 1991-1-5:2004 Part 1-5:
- General actions – Thermal actions
- UNI EN 1991-1-6:2005 Part 1-6:
- General actions – Actions during execution
- UNI EN 1991-1-7:2006 Part 1-7:
- General actions – Accidental actions
- UNI EN 1991-2:2005 Part 2:
- Traffic loads on bridges
- UNI EN 1991-3:2006 Part 3:
- Actions induced by cranes and machinery
- UNI EN 1991-4:2006 Part 4:
- Silos and tanks
Eurocode 3 – Design of steel structures
- UNI EN 1993-1-1:2005 Part 1-1:
- General rules and rules for buildings
- UNI EN 1993-1-2:2005 Part 1-2:
- General rules – Structural fire design
- UNI EN 1993-1-3:2007 Part 1-3:
- General rules – Supplementary rules for cold-formed members and sheeting
- UNI EN 1993-1-4:2007 Part 1-4:
- General rules – Supplementary rules for stainless steels
- UNI EN 1993-1-5:2007 Part 1-5:
- Plated structural elements
- UNI EN 1993-1-6:2007 Part 1-6:
- Strength and stability of shell structures
- UNI EN 1993-1-7:2007 Part 1-7:
- General rules – Strength and stability of planar plated structures subject to out of plane loading
- UNI EN 1993-1-8:2005 Part 1-8:
- Design of joints
- UNI EN 1993-1-9:2005 Part 1-9:
- Fatigue
- UNI EN 1993-1-10:2005 Part 1-10:
- MMterial toughness and through-thickness properties
- UNI EN 1993-1-11:2007 Part 1-11:
- Design of structures with tension components
- UNI EN 1993-1-12:2007 Part 1-12:
- General high strength steels (grade S700)
- UNI EN 1993-2:2007 Part 2:
- Steel bridges
- UNI EN 1993-3-1:2007 Part 3-1:
- Towers, masts and chimneys – Towers and masts
- UNI EN 1993-3-2:2007 Part 3-2:
- Towers, masts and chimneys – Chimneys
- UNI EN 1993-4-1:2007 Part 4-1:
- Silos
- UNI EN 1993-4-2:2007 Part 4-2:
- Tanks
- UNI EN 1993-4-3:2007 Part 4-3:
- Pipeline
- UNI EN 1993-5:2007 Part 5:
- Piling
- UNI EN 1993-6:2007 Part 6:
- Crane supporting structures
Eurocodice 5 – Design of timber structures
- UNI EN 1995-1-1:2014 Part 1-1:
- General rules – Common rules and rules for buildings
- UNI EN 1995-1-2:2005 Part 1-2:
- General rules – Structural fire design
- UNI EN 1995-2:2005 Part 2:
- Bridges
Eurocodice 7 – Design geotechnical
- UNI EN 1997-1:2005 Part 1:
- General rules
- UNI EN 1997-2:2007 Part 2:
- Ground investigation and testing (design assisted by field testing – previously part 3)



